- Review Article
- Open access
- Published:
Hormonal Regulators of Appetite
International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology volume 2009, Article number: 141753 (2008)
Abstract
Obesity is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. There has been a significant worsening of the obesity epidemic mainly due to alterations in dietary intake and energy expenditure. Alternatively, cachexia, or pathologic weight loss, is a significant problem for individuals with chronic disease. Despite their obvious differences, both processes involve hormones that regulate appetite. These hormones act on specific centers in the brain that affect the sensations of hunger and satiety. Mutations in these hormones or their receptors can cause substantial pathology leading to obesity or anorexia. Identification of individuals with specific genetic mutations may ultimately lead to more appropriate therapies targeted at the underlying disease process. Thus far, these hormones have mainly been studied in adults and animal models. This article is aimed at reviewing the hormones involved in hunger and satiety, with a focus on pediatrics.
1. Introduction
Obesity is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in the US and worldwide. Obesity in adults and children increases the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus [1], cardiovascular disease [2], and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [3], as well as psychosocial and social disturbances [4]. Significantly, obese children have an increased likelihood of becoming obese adults compared with children who are not obese [5]. And the incidence of childhood obesity is rising: during 2003-2004, 17.1% of children ( 20 years) had body mass indexes (BMIs)
20 years) had body mass indexes (BMIs)  95% for age and sex [6]. Increases in weight in the pediatric population are on the rise; by the year 2010, almost 50% of North American children and 38% of European children are expected to be overweight [7]. This forecast represents a long-term trend: surveys since 1963 have documented increasing numbers of overweight and obese children, and the rate of increase is accelerating [8, 9]. Overweight children were heavier in 1998 compared with 1986 [10]. Not surprisingly, BMI has also continued to increase with a shifting of the normal population bell-shaped curve to the right.
95% for age and sex [6]. Increases in weight in the pediatric population are on the rise; by the year 2010, almost 50% of North American children and 38% of European children are expected to be overweight [7]. This forecast represents a long-term trend: surveys since 1963 have documented increasing numbers of overweight and obese children, and the rate of increase is accelerating [8, 9]. Overweight children were heavier in 1998 compared with 1986 [10]. Not surprisingly, BMI has also continued to increase with a shifting of the normal population bell-shaped curve to the right.
At the other end of the spectrum, children with chronic diseases are significantly affected by weight loss, or cachexia, that includes "pathologic wasting of either muscle or muscle and fat tissue" [11]. Key features of cachexia include anorexia or decreased appetite despite weight below the physiologic set point, an accelerated loss of lean body tissues, and lack of a protective decrease in basal metabolic rate as weight continues to be lost. Cachexia has been found to be associated with such chronic illnesses as congenital heart disease [12], Crohn disease [13], renal failure [14, 15], and cancer [16, 17]. While the underlying cause of cachexia in chronic disease is complex, most authors agree that increased production of proinflammatory cytokines leads to many of the pathological features observed in this condition [18]. These cytokines interact directly and indirectly with centers in the brain that control appetite and basal metabolic rate and also have important direct effects on peripheral tissues.
Although great progress has been made in understanding the hormonal players that regulate appetite in adults, and therefore contribute to obesity and its opposite cachexia, these insights have not yet been applied to the pediatric population. This article will review the key hormonal players involved in hunger and satiety and how these hormones directly affect the brain. We will also review how humans and animals with mutations in these hormones or their receptors develop substantial pathology. Such mutations may increase the risk of developing obesity or disease-associated cachexia. Finally, we will discuss how hormone replacement or supplementation can offer a therapeutic option for obesity or cachexia. Much work has been done in adults and animal models. Here, we will attempt to address how these insights might affect pediatric practice and highlight the importance in children.
2. Hunger
2.1. The Role of The Hypothalamus in Stimulating Appetite
The hypothalamus acts as the control center for hunger and satiety. Part of the hypothalamus, the arcuate nucleus (or, in humans, the infundibular nucleus), allows entry through the blood-brain barrier of peripheral peptides and proteins that directly interact with its neurons. These include neurons that coexpress peptides that stimulate food intake and weight gain, specifically, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP), as well as those expressing pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) which inhibit feeding and promote weight loss (see Table 1). Together, these neurons and peptides control the sensations of hunger and satiety and ultimately weight gain and weight loss.
NPY is part of the pancreatic polypeptide (PP-)fold peptide family (NPY, polypeptide YY (PYY), PP). The medial arcuate nucleus contains the NPY neurons which project to the paraventricular nucleus, hypothalamic nucleus, lateral hypothalamic area, and other hypothalamic sites. NPY synthesis and release are regulated by leptin and insulin (both inhibitory), and glucocorticoids and ghrelin (both stimulatory), among many other factors. The most noticeable physiological response to central administration of NPY is the stimulation of feeding [19]. NPY initiates appetite drive through the NPY G-protein coupled receptors (primarily Y1 and Y5). NPY also represses the anorexigenic effect of melanocortin signaling in the arcuate. In the hypothalamus, NPY is one of the most abundant peptides and one of the most potent orexigenic factors.
AgRP is produced by neurons located within the medial arcuate nucleus that coexpress NPY. AgRP in humans has sequence similarity to the agouti signaling protein in mice. The agouti protein is a paracrine-signaling molecule produced normally in the skin that inhibits the effect of  -melanocyte stimulating hormone (
-melanocyte stimulating hormone ( -MSH) on the melanocortin-1 (MC-1) receptor [20]. Overexpression of agouti signaling protein in mice leads to yellow coat color by blocking
-MSH) on the melanocortin-1 (MC-1) receptor [20]. Overexpression of agouti signaling protein in mice leads to yellow coat color by blocking  -MSH at the MC-1 receptor. These mice are also obese, insulin resistant, hyperglycemic, and have increased body length [21]. This is because AgRP, an endogenous antagonist (and inverse agonist) of melanocortin-3 and melanocortin-4 receptors, is implicated in control of energy balance [22]. Blockage of these receptors leads to stimulation of feeding.
-MSH at the MC-1 receptor. These mice are also obese, insulin resistant, hyperglycemic, and have increased body length [21]. This is because AgRP, an endogenous antagonist (and inverse agonist) of melanocortin-3 and melanocortin-4 receptors, is implicated in control of energy balance [22]. Blockage of these receptors leads to stimulation of feeding.
2.2. The Peripheral Peptide That Stimulates Appetite
Circulating peptides also play important roles in appetitive behaviors. Of these, ghrelin, or growth hormone (GH)-releasing peptide, is the only known circulating orexigen, or appetite stimulant. It is mainly produced by the endocrine cells of the gastric mucosa of the fundus, but is also found in much smaller amounts in other tissues, including the small intestine, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, pancreas, lung, immune cells, placenta, ovary, testis, and kidney. Ghrelin levels rise prior to meals, then fall quickly after ingestion of nutrients [23]. Thus it is postulated that one primary role of ghrelin is to act as a meal initiator.
The ghrelin receptor, GH secretagogue receptor type 1a (GHS-R1a), is a G-protein coupled receptor that is widely expressed. Within the CNS, it is found in areas involved in the regulation of appetite and energy balance, including the hypothalamic nuclei, dorsal vagal complex, and mesolimbic dopaminergic system. Ghrelin has multiple effects, including stimulation of GH, ACTH, cortisol, aldosterone, catecholamine, and prolactin secretion. Exogenous ghrelin administration has also been found to affect glucose homeostasis, gut motility, pancreatic exocrine secretion, cardiovascular function, immunity, and inflammation [24]. Intracerebroventricular administration of ghrelin in rats leads to increased food intake, excess weight gain, and adiposity [25]. Similarly, administration of ghrelin to obese and lean human subjects leads to increased food intake [26]. Ghrelin leads to this increase of food intake and body weight in part by stimulating the production of NPY and AgRP in the arcuate nucleus [27]. Ghrelin may also alter energy balance by stimulating adipogenesis, inhibiting apoptosis, transitioning from fatty acid oxidation to glycolysis for energy expenditure, and inhibiting sympathetic nervous system activity [28–31].
Globally, ghrelin levels reflect nutritional status and body fat stores. Ghrelin levels in humans are inversely correlated with adiposity, being low in obese subjects, higher in lean subjects, and markedly elevated in subjects with cachexia due to cancer and chronic cardiac failure, as well as those in starvation states such as anorexia nervosa [32–37]. An exception to this is Prader-Willi syndrome, where, despite obesity, affected individuals have high levels of fasting and postprandial ghrelin [38]. Ghrelin treatment in rats has been shown to improve weight gain and lean body mass retention in cancer cachexia and chronic kidney disease [39, 40], offering a potential therapy for cachexia in humans. Alternatively, future studies may examine ghrelin antagonists as a therapeutic option for obesity.
3. Satiety
3.1. The Role of The Hypothalamus in Regulating Appetite
The hypothalamus is also the master regulator of satiety, via production of POMC and CART. The POMC gene is expressed by multiple tissues, including the skin and immune system, as well as the pituitary gland and the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. POMC undergoes tissue-specific post-translational cleavage, with the product depending on the endoproteases expressed in that tissue. For example, in the anterior pituitary gland, POMC is primarily converted to ACTH by prohormone convertase 1. In mammals other than primates, prohormone convertase 2 in the intermediate pituitary cleaves ACTH to yield  -melanocyte stimulating hormone (
-melanocyte stimulating hormone ( -MSH) that is involved in the control of coat/skin color. With respect to the hypothalamus in humans, leptin (a peptide produced by adipose tissue) is thought to stimulate POMC conversion into
-MSH) that is involved in the control of coat/skin color. With respect to the hypothalamus in humans, leptin (a peptide produced by adipose tissue) is thought to stimulate POMC conversion into  -MSH in the arcuate nucleus. The neurotransmitter in turn binds to the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R), a key receptor involved in appetite control and energy homeostasis, in the paraventricular nucleus and in numerous other sites throughout the brain.Intracerebroventricular administration of
-MSH in the arcuate nucleus. The neurotransmitter in turn binds to the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R), a key receptor involved in appetite control and energy homeostasis, in the paraventricular nucleus and in numerous other sites throughout the brain.Intracerebroventricular administration of  -MSH in rodents inhibits feeding and reduces body weight. As previously mentioned, AgRP is an antagonist of MC4R. Thus, mice overexpressing AgRP or MC4R knockout mice are hyperphagic and obese [41] and are insensitive to
-MSH in rodents inhibits feeding and reduces body weight. As previously mentioned, AgRP is an antagonist of MC4R. Thus, mice overexpressing AgRP or MC4R knockout mice are hyperphagic and obese [41] and are insensitive to  -MSH.
-MSH.
MC4R mutations have been found in up to 5.8% of adults with severe childhood-onset obesity [42]. POMC deficiency also leads to obesity (due to lack of binding at MC4R), hypocortisolism (due to lack of binding of ACTH to the MC2R in the adrenal gland), and alteration of pigment (due to lack of binding at MC1R in the skin). This syndrome is defined by severe early onset obesity, adrenal insufficiency, and red hair [43]. Accordingly, in rodent models of cancer and renal failure, MC4R receptor antagonists attenuate symptoms of cachexia by maintaining appetite, lean body mass, and basal energy expenditure [44]. Thus, MC4R antagonists may be a useful clinical treatment of cachexia [45], while agonists are being developed to treat obesity.
Another important satiety regulator in the hypothalamus is cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART), which is coexpressed with POMC in arcuate neurons in animal models and somewhat paradoxically with AgRP and NPY in humans [46]. Similar to POMC neurons, CART neurons are directly stimulated by leptin [47]. CART neurons target areas throughout the hypothalamus and are associated with reinforcement and reward [48], sensory processing, and stress and endocrine regulation [47, 49]. Animals deprived of food have decreased the expression of CART mRNA [47]. Along those same lines, blocking CART with an antiserum increases feeding in normal rats [50]. Intracerebroventricular administration of CART in rats inhibits normal and starvation-induced feeding, as well as blocking the NPY feeding response [47, 50]. At this point, we are not aware of any clinical trials utilizing CART agonists or antagonists for weight regulation perhaps due to the significant nonappetite effects associated with CART.
3.2. Peripheral Peptides Known to Control Satiety
In contrast to ghrelin, the single peripheral peptide known to stimulate hunger, there are many peripheral peptides that are associated with satiety. Various organs secrete these hormones, including the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, and adipose tissue. The list of satiety hormones is far too extensive to discuss in this review. We will, therefore, focus on the key players starting with cholecystokinin (CCK), the first discovered satiety hormone.
Cholecystokinin (CCK) was initially discovered in 1928 and was one of the first peptides to be found in the gut [51]. In addition to inhibiting food intake, CCK stimulates pancreatic secretion, gall bladder contraction, intestinal motility, and inhibition of gastric mobility. Administration of CCK to rats inhibits food intake by reducing meal size and duration [52], which is enhanced by gastric distention [53]. The half-life of CCK is only 1-2 minutes, therefore it is not effective at reducing meal size if administered more than 15 minutes before a meal [52].
CCK is synthesized throughout the gastrointestinal tract, but mainly in the duodenum and jejunum. Multiple bioactive forms are derived from the same gene product by posttranslational or extracellular processing. CCK is rapidly released locally and into the circulation in response to nutrients in the gut, especially fat and protein, with a gradual increase in levels over 10–30 minutes after meal initiation, remaining elevated for up to 5 hours [54].
CCK-sensitive brain sites include the lateral hypothalamus, medial pons, and lateral medulla. These areas are involved in reward behavior, memory and anxiety, as well as satiety [55, 56]. There are two types of G-protein coupled CCK receptors: CCK-A and CCK-B [57]. CCK-A is involved in satiety whereas CCK-B is not. CCK-A is found on the afferent vagal neurons that have a direct effect on food intake. Rats deficient in CCK-A (Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats) are hyperphagic, obese, and develop diabetes mellitus type 2 [58].
Another satiety peptide, peptide YY (PYY), is part of the pancreatic polypeptide (PP-) fold peptide family (NPY, PYY, PP), all of which have 36 amino acids, contain several tyrosine residues, and require C-terminal amidation for biologic activity. The PP-fold family exerts their effects via the Y family of G-protein coupled receptors (Y1, Y2, Y4, Y5) that are expressed in the hypothalamus. PYY is produced by the intestinal L cells of the ileum, colon, and rectum. Following food intake, PYY is released into the circulation and peaks 1-2 hours postprandially [59]. PYY concentrations are proportional to meal energy content and are therefore higher after fat intake compared to carbohydrates and proteins [60]. Circulating PYY exists in two forms:  and
and  .
.  is the peripherally active anorectic signal and is created by cleavage of the N-terminal Tyr-Pro residues by dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) [61].
is the peripherally active anorectic signal and is created by cleavage of the N-terminal Tyr-Pro residues by dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) [61]. binds to Y2 receptors leading to inhibition of NPY neurons and stimulation of POMC neurons.
binds to Y2 receptors leading to inhibition of NPY neurons and stimulation of POMC neurons.
Administration of PYY delays gastric emptying, inhibits secretions from the pancreas and stomach, inhibits gallbladder contraction, and increases the absorption of fluid and electrolytes from the ileum [62]. In rodents, the administration of PYY decreases food intake and reduces weight gain [63], as well as, improvesglycemic control in rodent models of diabetes [64]. PYY-deficient mice are resistant to satiety and develop marked obesity, which is reversed by exogenous PYY administration [65]. In contrast, intracerebroventricular administration of full length PYY stimulates food intake. This is thought to be via action on Y1 and Y5 receptors in the paraventricular nucleus, the neurons targeted by the orexigenic arcuate nucleus NPY neurons.
In obese and lean humans, administration of  decreases food intake with a significant decrease in the cumulative 24 hour caloric intake [66]. Obese subjects, however, have a lower endogenous PYY response at each meal compared to normal weight volunteers [67]. This relative PYY deficiency may reduce satiety and could thus reinforce obesity. Obese patients treated by jejunoileal bypass surgery [68] or vertical-banded gastroplasty [69] have elevated PYY levels, which may contribute to their appetite loss.
decreases food intake with a significant decrease in the cumulative 24 hour caloric intake [66]. Obese subjects, however, have a lower endogenous PYY response at each meal compared to normal weight volunteers [67]. This relative PYY deficiency may reduce satiety and could thus reinforce obesity. Obese patients treated by jejunoileal bypass surgery [68] or vertical-banded gastroplasty [69] have elevated PYY levels, which may contribute to their appetite loss.
Pancreatic polypeptide (PP), another member of the PP-fold peptide family, is produced largely in the endocrine pancreas, and also in the exocrine pancreas, colon, and rectum. PP is also released in response to a meal, in proportion to caloric load, and inhibits appetite [70]. PP release is stimulated by ghrelin, as well as motilin (a peptide secreted by the small intestine that enhances gastrointestinal motility) and secretin (a peptide secreted by the duodenum that stimulates gastric acid secretion), whereas somatostatin (a hormone that decreases the rate of gastric emptying, and reduces smooth muscle contraction and blood flow within the intestine) and its analogs significantly reduce PP secretion. PP binds with greatest affinity to the Y4 and Y5 receptors [71]. Peripheral administration of PP in normal mice reduces food intake, gastric emptying, and gastric expression of ghrelin, while it increases vagal tone [72]. Similar to PYY, injection of PP into the third ventricle stimulates daytime food intake [73]. Interestingly, patients with Prader-Willi syndrome have suppressed basal and postprandial PP levels [74]. Administration of PP in Prader-Willi patients leads to reduced food intake [75].
Incretins are hormones released from the gastrointestinal tract into the circulation in response to nutrient ingestion. Incretins enhance glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Preproglucagon is expressed in the  cells of the endocrine pancreas, L cells of the intestine (distal ileum and colon), and neurons located in the caudal brainstem and hypothalamus. It is cleaved into multiple different products, including glucagon and two of the incretins, oxyntomodulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Oxyntomodulin and GLP-1 are released from L cells in the distal ileum and colon in response to ingestion of nutrients. Oxyntomodulin binds the GLP-1 receptor that is expressed in the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem and in the arcuate nucleus. Oxyntomodulin inhibits gastric acid secretion, decreases gastric emptying, and decreases pancreatic enzyme secretion which is likely related to decreased gastric output [76]. Administration of oxyntomodulin in humans has been found to suppress ghrelin levels [77], decrease body weight and appetite, decrease leptin, and increase adiponectin levels presumably secondary to loss of adipose tissue [78].
cells of the endocrine pancreas, L cells of the intestine (distal ileum and colon), and neurons located in the caudal brainstem and hypothalamus. It is cleaved into multiple different products, including glucagon and two of the incretins, oxyntomodulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Oxyntomodulin and GLP-1 are released from L cells in the distal ileum and colon in response to ingestion of nutrients. Oxyntomodulin binds the GLP-1 receptor that is expressed in the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem and in the arcuate nucleus. Oxyntomodulin inhibits gastric acid secretion, decreases gastric emptying, and decreases pancreatic enzyme secretion which is likely related to decreased gastric output [76]. Administration of oxyntomodulin in humans has been found to suppress ghrelin levels [77], decrease body weight and appetite, decrease leptin, and increase adiponectin levels presumably secondary to loss of adipose tissue [78].
GLP-1 leads to delay in gastric emptying, stimulation of glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibition of glucagon secretion, and stimulation of somatostatin secretion. GLP-1 binds to its receptor, a G-protein coupled receptor that belongs to the class B family, including receptors for glucagon and GIP [79]. The GLP-1 receptor is expressed in a wide range of tissues, including the pancreatic islet cells, lung, heart, kidney, stomach, intestine, pituitary, skin, vagus nerve, and several regions of the CNS including the hypothalamus and brainstem. Peripheral and central GLP-1 administration activates neurons in the arcuate and paraventricular nuclei, nucleus of the solitary tract, and area postrema [80] leading to decreased appetite. GLP-1 administration promotes satiety and has beneficial effects on glucose homeostasis.
The properties of GLP-1 have made it a useful drug target. GLP-1 is released rapidly into the circulation after oral nutrient ingestion, and its secretion occurs in a biphasic pattern starting with an early (within 10–15 minutes) phase that is followed by a longer (30–60 minutes) phase [81]. The half-life of GLP-1 is less than 2 minutes owing to rapid inactivation by the enzyme DPP-IV, which also cleaves PYY. This is the basis for the development of exenatide (Byetta), a subcutaneously administered DPP-IV-resistant GLP-1 receptor agonist.
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) is another incretin that is secreted by the stomach and K cells in the duodenum and jejunum in response to nutrient ingestion. The half-life of GIP is 7 minutes in healthy individuals and 5 minutes in patients with type 2 diabetes [82]. GIP is also inactivated by DPP-IV [82, 83]. The GIP receptor gene is expressed in the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, adipose tissue, adrenal cortex, pituitary, heart, testis, endothelial cells, bone, trachea, spleen, thymus, lung, kidney, thyroid, and several regions in the CNS. GIP leads to glucose-dependent insulin secretion, induction of  cell proliferation, promotion of energy storage via direct actions on adipose tissue, and enhancement of bone formation via stimulation of osteoblast proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. In the CNS, GIP is expressed in the hippocampus and GIP receptor expression is detected in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb. GIP action in the CNS may play a role in neural progenitor cell proliferation and behavior modification [84].
cell proliferation, promotion of energy storage via direct actions on adipose tissue, and enhancement of bone formation via stimulation of osteoblast proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. In the CNS, GIP is expressed in the hippocampus and GIP receptor expression is detected in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb. GIP action in the CNS may play a role in neural progenitor cell proliferation and behavior modification [84].
Insulin is another hormonal regulator of appetite. Insulin levels increase rapidly after a meal and vary directly with changes in adiposity. Insulin penetrates the blood-brain barrier via a saturatable, receptor-mediated process at levels proportional to the circulating insulin [85]. Insulin receptors are widely distributed in the brain with highest concentrations found in the olfactory bulbs and arcuate nucleus. Once insulin enters the brain, it acts as an anorexigenic signal [86]. Mice with a neuron-specific disruption of the insulin receptor gene have increased food intake, obesity with increased body fat, and plasma leptin levels, and impaired spermatogenesis and ovarian follicle maturation [87]. There are several insulin receptor substrates (IRS) that are activated by phosphorylation by the insulin receptor on their tyrosine residues [88]. IRS-1 and IRS-2 have been identified in neurons. IRS-2 knockout mice have been found to have increased food intake, increased fat stores, and infertility [89].
Leptin, also termed OB protein, is another important appetite regulator. It is produced by the white and brown adipose tissue, stomach, placenta, mammary gland, ovarian follicles, and certain fetal organs such as heart, bone or cartilage, and perhaps the brain. The ob gene is expressed in all adipose tissue, but to a greater degree in the subcutaneous adipose tissue than the omental fat. Leptin levels are positively correlated with the amount of body fat mass. Leptin secretion does not appear to be driven by meal patterns. Instead, the circadian pattern is characterized by high levels between midnight and early morning hours and a nadir around noon to midafternoon [90]. Leptin is secreted in a pulsatile fashion with 32 peaks per 24-hour period and a pulse duration of 32.8 minutes [91]. This implies that neural and neurohormonal components in the brain may regulate leptin secretion from adipocytes.
Leptin receptors belong to the cytokine receptor superfamily, which uses the Janus activating kinase (JAK-) signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway of signal transduction. Leptin receptors have multiple different splice variants. Ob-Rb is the long form of the receptor and has a long intracellular domain, which is necessary for the action of leptin on appetite. Ob-Rb is expressed in multiple different sites within the hypothalamus including the arcuate nucleus, paraventricular nucleus, dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus, and lateral hypothalamic area. Short forms of the Ob receptor may play a role in the transport of leptin across the blood-brain barrier [92]. After binding the receptor, leptin stimulates a specific signaling cascade that results in inhibition of orexigenic peptides (NPY and AgRP) [93, 94], while stimulating anorectic peptides (including POMC and CART) [93, 95]. Ultimately, this leads to decreased appetite and increased energy expenditure. db/db mice have a mutation in the intracellular portion of Ob-Rb and therefore are unable to respond to the leptin signal and as a result develop profound obesity [96]. Additionally, it has been found that up to 3% of individuals with severe early onset obesity have pathogenic mutations in the leptin-receptor gene [97].
Ob-deficient mice have an absence of circulating leptin and develop severe obesity due to both increased food intake and decreased energy expenditure [98], both of which can be normalized by the administration of leptin [99]. The absence of leptin in humans leads to severe obesity, hypogonadism, and impaired T cell mediated immunity, which are remediable with administration of recombinant leptin [100]. About 5% of obese populations are "relatively" leptin deficient and it is possible that these individuals could benefit from leptin therapy [101].
Finally, the hormone adiponectin is secreted by the mature adipocyte. Adiponectin receptors are expressed in the brain, particularly in the paraventricular nucleus, amygdala, area postrema, and diffusely in the periventricular areas. For reasons that are unclear, adiponectin's concentration in the blood stream is extremely high, approximately 1000 times higher than that of other polypeptide hormones. Its structure closely resembles C1q and types VIII and X collagen. Generally, adiponectin self associates to form homotrimers that then dimerize to yield hexamers. Increased adiponectin levels in rodents appear to decrease body fat mass by stimulation of fatty acid oxidation in muscle [102]. Adiponectin also decreases food intake and obesity in obese rats [103], and improves insulin sensitivity by decreasing hepatic glucose output [104]. In humans, high molecular weight adiponectin (which is thought to be the active form) is reduced in patients with type 2 diabetes, and increasing the proportion of high molecular weight adiponectin by weight loss and treatment with thiazolinediones leads to improved insulin sensitivity [105].
4. Suggestions in Children
Although the obesity epidemic has worsened significantly in children presumably owing to alterations in dietary intake and energy expenditure, there have been clearly demonstrable genetic mutations in hormones and their receptors that may be implicated in childhood obesity. It would therefore be important to identify children with early onset obesity that is resistant to dietary modification and physical activity to evaluate them for possible genetic mutations. This could lead to more appropriate therapies targeted at the underlying disease process. It has also become clear that certain acquired pathological states associated with childhood obesity may respond well to specific-targeted therapy based on the underlying pathology. For example, the intense hyperphagia and weight gain frequently observed after damage of the basal hypothalamus (e.g., commonly observed after resection of a craniopharyngioma) may be due to the loss of the inhibitory tone provided by POMC neurons. In this case, treatment with a melanocortin agonist may be particularly beneficial. In contrast, patients with Prader-Willi syndrome may be more likely to benefit from therapies that restore normal physiological levels of peripheral appetite regulating hormones, such as ghrelin antagonists.
Similarly, one might also consider hormonal agonists or antagonists as treatments of cachexia. Several preclinical and clinical trials indicate that GHS-1 R agonists (including ghrelin itself) are effective agents for this particular metabolic derangement. Other models suggest that melanocortin-4 receptor antagonists will also provide effective therapy for cachexia and involuntary weight loss. Collectively, our understanding of the complex nature of weight regulation has opened the door to a more thoughtful approach to therapeutic intervention in disorders of weight regulation. The redundancy of these systems highlights the likelihood that no one single agent will be effective in every situation, making individualized combinations of therapy a more rational solution to weight regulation therapy.
References
Fagot-Campagna A, Pettitt DJ, Engelgau MM: Type 2 diabetes among North American children and adolescents: an epidemiologic review and a public health perspective. The Journal of Pediatrics. 2000, 136 (5): 664-672. 10.1067/mpd.2000.105141.
Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA: Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2006, 26 (5): 968-976. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000216787.85457.f3.
Clark JM: The epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. 2006, 40 (supplement 1): S5-S10.
Puhl RM, Latner JD: Stigma, obesity, and the health of the nation's children. Psychological Bulletin. 2007, 133 (4): 557-580. 10.1037/0033-2909.133.4.557.
Serdula MK, Ivery D, Coates RJ, Freedman DS, Williamson DF, Byers T: Do obese children become obese adults? A review of the literature. Preventive Medicine. 1993, 22 (2): 167-177. 10.1006/pmed.1993.1014.
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM: Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2006, 295 (13): 1549-1555. 10.1001/jama.295.13.1549.
Wang Y, Lobstein T: Worldwide trends in childhood overweight and obesity. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity. 2006, 1 (1): 11-25. 10.1080/17477160600586747.
Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM: The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007, 132 (6): 2087-2102. 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.052.
Troiano RP, Flegal KM, Kuczmarski RJ, Campbell SM, Johnson CL: Overweight prevalence and trends for children and adolescents. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1963 to 1991. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 1995, 149 (10): 1085-1091. 10.1001/archpedi.1995.02170230039005.
Strauss RS, Pollack HA: Epidemic increase in childhood overweight, 1986–1998. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2001, 286 (22): 2845-2848. 10.1001/jama.286.22.2845.
Springer J, von Haehling S, Anker SD: The need for a standardized definition for cachexia in chronic illness. Nature Clinical Practice Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2006, 2 (8): 416-417. 10.1038/ncpendmet0247.
Hallioglu O, Alehan D, Kandemir N: Plasma leptin levels in children with cyanotic and acyanotic congenital heart disease and correlations with growth parameters. International Journal of Cardiology. 2003, 92 (1): 93-97. 10.1016/S0167-5273(03)00044-5.
Burnham JM, Shults J, Semeao E: Body-composition alterations consistent with cachexia in children and young adults with Crohn disease. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2005, 82 (2): 413-420.
Mak RH, Cheung W, Cone RD, Marks D: Mechanisms of disease: cytokine and adipokine signaling in uremic cachexia. Nature Clinical Practice Nephrology. 2006, 2 (9): 527-534. 10.1038/ncpneph0273.
Mak RH, Cheung W: Cachexia in chronic kidney disease: role of inflammation and neuropeptide signaling. Hormones, autacoids, neurotransmitters and growth factors. Current Opinion in Nephrology & Hypertension. 2007, 16 (1): 27-31. 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3280117ce7.
Lai J-S, Cella D, Peterman A, Barocas J, Goldman S: Anorexia/cachexia-related quality of life for children with cancer: testing the psychometric properties of the pediatric functional assessment of anorexia and cachexia therapy (peds-FAACT). Cancer. 2005, 104 (7): 1531-1539. 10.1002/cncr.21315.
Baracos VE: Cancer-associated cachexia and underlying biological mechanisms. Annual Review of Nutrition. 2006, 26 (1): 435-461. 10.1146/annurev.nutr.26.061505.111151.
Morley JE, Thomas DR, Wilson M-MG: Cachexia: pathophysiology and clinical relevance. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2006, 83 (4): 735-743.
Stanley BG, Kyrkouli SE, Lampert S, Leibowitz SF: Neuropeptide Y chronically injected into the hypothalamus: a powerful neurochemical inducer of hyperphagia and obesity. Peptides. 1986, 7 (6): 1189-1192. 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90149-X.
Leibel RL, Chung WK, Chua SC: The molecular genetics of rodent single gene obesities. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997, 272 (51): 31937-31940. 10.1074/jbc.272.51.31937.
Ollmann MM, Lamoreux ML, Wilson BD, Barsh GS: Interaction of Agouti protein with the melanocortin 1 receptor in vitro and in vivo. Genes & Development. 1998, 12 (3): 316-330. 10.1101/gad.12.3.316.
Yang Y-K, Thompson DA, Dickinson CJ: Characterization of Agouti-related protein binding to melanocortin receptors. Molecular Endocrinology. 1999, 13 (1): 148-155. 10.1210/me.13.1.148.
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS: A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes. 2001, 50 (8): 1714-1719. 10.2337/diabetes.50.8.1714.
van der Lely AJ, Tschöp M, Heiman ML, Ghigo E: Biological, physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocrine Reviews. 2004, 25 (3): 426-457. 10.1210/er.2002-0029.
Wren AM, Small CJ, Abbott CR: Ghrelin causes hyperphagia and obesity in rats. Diabetes. 2001, 50 (11): 2540-2547. 10.2337/diabetes.50.11.2540.
Druce MR, Wren AM, Park AJ: Ghrelin increases food intake in obese as well as lean subjects. International Journal of Obesity. 2005, 29 (9): 1130-1136. 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803001.
Greenman Y, Golani N, Gilad S, Yaron M, Limor R, Stern N: Ghrelin secretion is modulated in a nutrient- and gender-specific manner. Clinical Endocrinology. 2004, 60 (3): 382-388. 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2004.01993.x.
Choi K, Roh S-G, Hong Y-H: The role of ghrelin and growth hormone secretagogues receptor on rat adipogenesis. Endocrinology. 2003, 144 (3): 754-759. 10.1210/en.2002-220783.
Matsumura K, Tsuchihashi T, Fujii K, Abe I, Iida M: Central ghrelin modulates sympathetic activity in conscious rabbits. Hypertension. 2002, 40 (5): 694-699. 10.1161/01.HYP.0000035395.51441.10.
Thompson NM, Gill DAS, Davies R: Ghrelin and des-octanoyl ghrelin promote adipogenesis directly in vivo by a mechanism independent of the type 1a growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Endocrinology. 2004, 145 (1): 234-242. 10.1210/en.2003-0899.
Tschop M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML: Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000, 407 (6806): 908-913. 10.1038/35038090.
Nagaya N, Uematsu M, Kojima M: Elevated circulating level of ghrelin in cachexia associated with chronic heart failure: relationships between ghrelin and anabolic/catabolic factors. Circulation. 2001, 104 (17): 2034-2038. 10.1161/hc4201.097836.
Otto B, Cuntz U, Fruehauf E: Weight gain decreases elevated plasma ghrelin concentrations of patients with anorexia nervosa. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2001, 145 (5): 669-673.
Shiiya T, Nakazato M, Mizuta M: Plasma ghrelin levels in lean and obese humans and the effect of glucose on ghrelin secretion. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2002, 87 (1): 240-244. 10.1210/jc.87.1.240.
Shimizu Y, Nagaya N, Isobe T: Increased plasma ghrelin level in lung cancer cachexia. Clinical Cancer Research. 2003, 9 (2): 774-778.
Tolle V, Kadem M, Bluet-Pajot M-T: Balance in Ghrelin and leptin plasma levels in anorexia nervosa patients and constitutionally thin women. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2003, 88 (1): 109-116. 10.1210/jc.2002-020645.
Tschöp M, Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Devanarayan V, Ravussin E, Heiman ML: Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes. 2001, 50 (4): 707-709. 10.2337/diabetes.50.4.707.
Cummings DE, Clement K, Purnell JQ: Elevated plasma ghrelin levels in Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature Medicine. 2002, 8 (7): 643-644. 10.1038/nm0702-643.
DeBoer MD, Zhu X, Levasseur PR: Ghrelin treatment of chronic kidney disease: improvements in lean body mass and cytokine profile. Endocrinology. 2008, 149 (2): 827-835. 10.1210/en.2007-1046.
DeBoer MD, Xin XZ, Levasseur P: Ghrelin treatment causes increased food intake and retention of lean body mass in a rat model of cancer cachexia. Endocrinology. 2007, 148 (6): 3004-3012. 10.1210/en.2007-0016.
Huszar D, Lynch CA, Fairchild-Huntress V: Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell. 1997, 88 (1): 131-141. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81865-6.
Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, Yeo GSH, Lank EJ, Cheetham T, O'Rahilly S: Clinical spectrum of obesity and mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor gene. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003, 348 (12): 1085-1095. 10.1056/NEJMoa022050.
Krude H, Biebermann H, Schnabel D: Obesity due to proopiomelanocortin deficiency: three new cases and treatment trials with thyroid hormone and ACTH4-10. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2003, 88 (10): 4633-4640. 10.1210/jc.2003-030502.
DeBoer MD, Marks D: Therapy insight: use of melanocortin antagonists in the treatment of cachexia in chronic disease. Nature Clinical Practice Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2006, 2 (8): 459-466. 10.1038/ncpendmet0221.
Foster AC, Chen C, Markison S, Marks D: MC4 receptor antagonists: a potential treatment for cachexia. IDrugs. 2005, 8 (4): 314-319.
Menyhért J, Wittmann G, Lechan RM, Keller É, Liposits Z, Fekete C: Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) is colocalized with the orexigenic neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein and absent from the anorexigenic
 -melanocyte-stimulating hormone neurons in the infundibular nucleus of the human hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 2007, 148 (9): 4276-4281. 10.1210/en.2007-0390.
-melanocyte-stimulating hormone neurons in the infundibular nucleus of the human hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 2007, 148 (9): 4276-4281. 10.1210/en.2007-0390.Kristensen P, Judge ME, Thim L: Hypothalamic CART is a new anorectic peptide regulated by leptin. Nature. 1998, 393 (6680): 72-76. 10.1038/29993.
Koylu EO, Couceyro PR, Lambert PD, Kuhar MJ: Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide immunohistochemical localization in the rat brain. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1998, 391 (1): 115-132. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19980202)391:1<115::AID-CNE10>3.0.CO;2-X.
Stanley SA, Small CJ, Murphy KG: Actions of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptide on regulation of appetite and hypothalamo-pituitary axes in vitro and in vivo in male rats. Brain Research. 2001, 893 (1-2): 186-194. 10.1016/S0006-8993(00)03312-6.
Lambert PD, Couceyro PR, Mcgirr KM, Dall Vechia SE, Smith Y, Kuhar MJ: CART peptides in the central control of feeding and interactions with neuropeptide Y. Synapse. 1998, 29 (4): 293-298. 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199808)29:4<293::AID-SYN1>3.0.CO;2-0.
Ivy AC, Oldberg E: A hormone mechanism for gall-bladder contraction and evacuation. The American Journal of Physiology. 1928, 86 (3): 599-613.
Gibbs J, Young RC, Smith GP: Cholecystokinin decreases food intake in rats. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology. 1973, 84 (3): 488-495. 10.1037/h0034870.
Kissileff HR, Carretta JC, Geliebter A, Pi-Sunyer FX: Cholecystokinin and stomach distension combine to reduce food intake in humans. The American Journal of Physiology. 2003, 285 (5): R992-R998.
Liddle RA, Goldfine ID, Rosen MS, Taplitz RA, Williams JA: Cholecystokinin bioactivity in human plasma. Molecular forms, responses to feeding, and relationship to gallbladder contraction. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1985, 75 (4): 1144-1152. 10.1172/JCI111809.
Schick RR, Schusdziarra V, Yaksh TL, Go VLW: Brain regions where cholecystokinin exerts its effect on satiety. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1994, 713: 242-254. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb44072.x.
Crawley JN, Corwin RL: Biological actions of cholecystokinin. Peptides. 1994, 15 (4): 731-755. 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90104-X.
Moran TH: Cholecystokinin and satiety: current perspectives. Nutrition. 2000, 16 (10): 858-865. 10.1016/S0899-9007(00)00419-6.
Moran TH, Katz LF, Plata-Salaman CR, Schwartz GJ: Disordered food intake and obesity in rats lacking cholecystokinin A receptors. The American Journal of Physiology. 1998, 274 (3): R618-R625.
Adrian TE, Ferri GL, Bacarese-Hamilton AJ, Fuessl HS, Polak JM, Bloom SR: Human distribution and release of a putative new gut hormone, peptide YY. Gastroenterology. 1985, 89 (5): 1070-1077.
Lin HC, Chey WY: Cholecystokinin and peptide YY are released by fat in either proximal or distal small intestine in dogs. Regulatory Peptides. 2003, 114 (2-3): 131-135. 10.1016/S0167-0115(03)00115-0.
Eberlein GA, Eysselein VE, Schaeffer M: A new molecular form of PYY: structural characterization of human PYY(3–36) and PYY(1–36). Peptides. 1989, 10 (4): 797-803. 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90116-2.
Adrian TE, Savage AP, Sagor GR: Effect of peptide YY on gastric, pancreatic, and biliary function in humans. Gastroenterology. 1985, 89 (3): 494-499.
Batterham RL, Cowley MA, Small CJ: Gut hormone
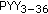 physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002, 418 (6898): 650-654. 10.1038/nature00887.
physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002, 418 (6898): 650-654. 10.1038/nature00887.Pittner RA, Moore CX, Bhavsar SP: Effects of PYY[3-36] in rodent models of diabetes and obesity. International Journal of Obesity. 2004, 28 (8): 963-971. 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802696.
Batterham RL, Heffron H, Kapoor S: Critical role for peptide YY in protein-mediated satiation and body-weight regulation. Cell Metabolism. 2006, 4 (3): 223-233. 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.08.001.
Batterham RL, Cohen MA, Ellis SM: Inhibition of food intake in obese subjects by peptide
 . The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003, 349 (10): 941-948. 10.1056/NEJMoa030204.
. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003, 349 (10): 941-948. 10.1056/NEJMoa030204.Le Roux CW, Batterham RL, Aylwin SJB: Attenuated peptide YY release in obese subjects is associated with reduced satiety. Endocrinology. 2006, 147 (1): 3-8. 10.1210/en.2005-0972.
Näslund E, Grybäck P, Hellström PM: Gastrointestinal hormones and gastric emptying 20 years after jejunoileal bypass for massive obesity. International Journal of Obesity. 1997, 21 (5): 387-392. 10.1038/sj.ijo.0800418.
Bartolomé MA, Borque M, Martinez-Sarmiento J: Peptide YY secretion in morbidly obese patients before and after vertical banded gastroplasty. Obesity Surgery. 2002, 12 (3): 324-327. 10.1381/096089202321088084.
Track NS, McLeod RS, Mee AV: Human pancreatic polypeptide: studies of fasting and postprandial plasma concentrations. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology. 1980, 58 (12): 1484-1489.
Larhammar D: Structural diversity of receptors for neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Regulatory Peptides. 1996, 65 (3): 165-174. 10.1016/0167-0115(96)00110-3.
Asakawa A, Inui A, Yuzuriha H: Characterization of the effects of pancreatic polypeptide in the regulation of energy balance. Gastroenterology. 2003, 124 (5): 1325-1336. 10.1016/S0016-5085(03)00216-6.
Clark JT, Kalra PS, Crowley WR, Kalra SP: Neuropeptide Y and human pancreatic polypeptide stimulate feeding behavior in rats. Endocrinology. 1984, 115 (1): 427-429. 10.1210/endo-115-1-427.
Zipf WB, O'Dorisio TM, Cataland S, Sotos J: Blunted pancreatic polypeptide responses in children with obesity of Prader-Willi syndrome. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 1981, 52 (6): 1264-1266. 10.1210/jcem-52-6-1264.
Berntson GG, Zipf WB, O'Dorisio TM, Hoffman JA, Chance RE: Pancreatic polypeptide infusions reduce food intake in Prader-Willi syndrome. Peptides. 1993, 14 (3): 497-503. 10.1016/0196-9781(93)90138-7.
Schjoldager B, Mortensen PE, Myhre J, Christiansen J, Holst JJ: Oxyntomodulin from distal gut. Role in regulation of gastric and pancreatic functions. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 1989, 34 (9): 1411-1419. 10.1007/BF01538078.
Cohen MA, Ellis SM, Le Roux CW: Oxyntomodulin suppresses appetite and reduces food intake in humans. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2003, 88 (10): 4696-4701. 10.1210/jc.2003-030421.
Wynne K, Park AJ, Small CJ: Subcutaneous oxyntomodulin reduces body weight in overweight and obese subjects: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes. 2005, 54 (8): 2390-2395. 10.2337/diabetes.54.8.2390.
Mayo KE, Miller LJ, Bataille D: International Union of Pharmacology. XXXV. The glucagon receptor family. Pharmacological Reviews. 2003, 55 (1): 167-194. 10.1124/pr.55.1.6.
Drucker DJ: The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metabolism. 2006, 3 (3): 153-165. 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.004.
Herrmann C, Göke R, Richter G, Fehmann H-C, Arnold R, Göke B: Glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulin releasing polypeptide plasma levels in response to nutrients. Digestion. 1995, 56 (2): 117-126. 10.1159/000201231.
Deacon CF, Nauck MA, Meier J, Hücking K, Holst JJ: Degradation of endogenous and exogenous gastric inhibitory polypeptide in healthy and in type 2 diabetic subjects as revealed using a new assay for the intact peptide. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2000, 85 (10): 3575-3581. 10.1210/jc.85.10.3575.
Kieffer TJ, McIntosh CHS, Pederson RA: Degradation of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and truncated glucagon-like peptide 1 in vitro and in vivo by dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Endocrinology. 1995, 136 (8): 3585-3596. 10.1210/en.136.8.3585.
Nyberg J, Anderson MF, Meister B: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide is expressed in adult hippocampus and induces progenitor cell proliferation. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2005, 25 (7): 1816-1825. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4920-04.2005.
Baura GD, Foster DM, Porte D: Saturable transport of insulin from plasma into the central nervous system of dogs in vivo. A mechanism for regulated insulin delivery to the brain. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1993, 92 (4): 1824-1830. 10.1172/JCI116773.
Woods SC, Lotter EC, McKay LD, Porte D: Chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of insulin reduces food intake and body weight of baboons. Nature. 1979, 282 (5738): 503-505. 10.1038/282503a0.
Brüning JC, Gautam D, Burks DJ: Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction. Science. 2000, 289 (5487): 2122-2125. 10.1126/science.289.5487.2122.
Cheatham B, Kahn CR: Insulin action and the insulin signaling network. Endocrine Reviews. 1995, 16 (2): 117-142.
Burks DJ, de Mora JF, Schubert M: IRS-2 pathways integrate female reproduction and energy homeostasis. Nature. 2000, 407 (6802): 377-382. 10.1038/35030105.
Sinha MK, Ohannesian JP, Heiman ML: Nocturnal rise of leptin in lean, obese, and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus subjects. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1996, 97 (5): 1344-1347. 10.1172/JCI118551.
Licinio J, Mantzoros C, Negrão AB: Human leptin levels are pulsatile and inversely related to pituitary-adrenal function. Nature Medicine. 1997, 3 (5): 575-579. 10.1038/nm0597-575.
Kastin AJ, Pan W: Dynamic regulation of leptin entry into brain by the blood-brain barrier. Regulatory Peptides. 2000, 92 (1–3): 37-43. 10.1016/S0167-0115(00)00147-6.
Elias CF, Aschkenasi C, Lee C: Leptin differentially regulates NPY and POMC neurons projecting to the lateral hypothalamic area. Neuron. 1999, 23 (4): 775-786. 10.1016/S0896-6273(01)80035-0.
van den Top M, Lee K, Whyment AD, Blanks AM, Spanswick D: Orexigen-sensitive NPY/AgRP pacemaker neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Nature Neuroscience. 2004, 7 (5): 493-494. 10.1038/nn1226.
Cowley MA, Smart JL, Rubinstein M: Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature. 2001, 411 (6836): 480-484. 10.1038/35078085.
Campfield LA, Smith FJ, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P: Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science. 1995, 269 (5223): 546-549. 10.1126/science.7624778.
Farooqi IS, Wangensteen T, Collins S: Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of congenital deficiency of the leptin receptor. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2007, 356 (3): 237-247. 10.1056/NEJMoa063988.
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM: Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994, 372 (6505): 425-432. 10.1038/372425a0.
Weigle DS, Bukowski TR, Foster DC: Recombinant ob protein reduces feeding and body weight in the ob/ob mouse. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1995, 96 (4): 2065-2070. 10.1172/JCI118254.
Farooqi IS, Matarese G, Lord GM: Beneficial effects of leptin on obesity, T cell hyporesponsiveness, and neuroendocrine/metabolic dysfunction of human congenital leptin deficiency. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2002, 110 (8): 1093-1103.
Sinha MK, Caro JF: Clinical aspects of leptin. Vitamins & Hormones. 1998, 54: 1-30. 10.1016/S0083-6729(08)60919-X.
Tomas E, Tsao T-S, Saha AK: Enhanced muscle fat oxidation and glucose transport by ACRP30 globular domain: acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibition and AMP-activated protein kinase activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2002, 99 (25): 16309-16313. 10.1073/pnas.222657499.
Shklyaev S, Aslanidi G, Tennant M: Sustained peripheral expression of transgene adiponectin offsets the development of diet-induced obesity in rats. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003, 100 (24): 14217-14222. 10.1073/pnas.2333912100.
Combs TP, Pajvani UB, Berg AH: A transgenic mouse with a deletion in the collagenous domain of adiponectin displays elevated circulating adiponectin and improved insulin sensitivity. Endocrinology. 2004, 145 (1): 367-383. 10.1210/en.2003-1068.
Pajvani UB, Hawkins M, Combs TP: Complex distribution, not absolute amount of adiponectin, correlates with thiazolidinedione-mediated improvement in insulin sensitivity. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004, 279 (13): 12152-12162. 10.1074/jbc.M311113200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Austin, J., Marks, D. Hormonal Regulators of Appetite. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol 2009, 141753 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/141753
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/141753
 -melanocyte-stimulating hormone neurons in the infundibular nucleus of the human hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 2007, 148 (9): 4276-4281. 10.1210/en.2007-0390.
-melanocyte-stimulating hormone neurons in the infundibular nucleus of the human hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 2007, 148 (9): 4276-4281. 10.1210/en.2007-0390.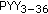 physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002, 418 (6898): 650-654. 10.1038/nature00887.
physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002, 418 (6898): 650-654. 10.1038/nature00887. . The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003, 349 (10): 941-948. 10.1056/NEJMoa030204.
. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003, 349 (10): 941-948. 10.1056/NEJMoa030204.